In order to carry out research, the role of literature reviews is crucial to draw together existing knowledge, identify gaps and inform future research. Systematic reviews and traditional literature reviews are among the popular types of literature review. Their methods, aims, and reliability vary considerably though each of them is facing the same goal which is summarizing the facts their dealing with. It is important for researchers and students to understand these differences if they are going to engage in producing not only good work but also potential-winning work.
What is a Conventional Literature Review?
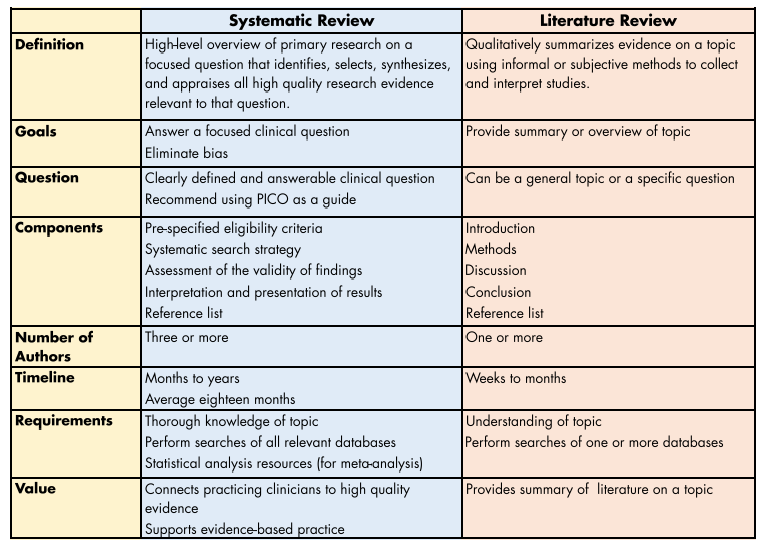
A narrative review (NR), also referred to as a conventional/literature review, is a qualitative study that qualitatively and interpretively summarizes another author’s piece of research. It uses several sources (scientific articles, books, reports) to give an overview of the domain. However, in a typical review, the literature is often selected subjectively according to the researcher’s preference and judgement. Or it may provide summary statistics of the research studies analyzed but will not summarize the individual studies or use a standard methodology of analysis.
Definition of a Systematic Review
A systematic review is a more systematic and structured method for reviewing the literature. Compared to narrative systematic review methodologies, systematic reviews adhere to a predetermined plan which is intended to identify, select and assess (critically) all available research on a given question. This is an explicit process which includes predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria, a systematic search of multiple databases and quality appraisal of each of the studies. The aim is to produce a neutral, transparent and reproducible synopsis of evidence around a topic.
Distinctions Between Systematic and Traditional Literature Review
- The methods are one of the first differences. Systematic reviews are performed in a transparent and stepwise manner, which makes them reproducible and relatively free from bias. In contrast, traditional reviews are typically more subjective, with the researcher making choices on the sources selected and how findings are interpreted.
- The purpose also differs. By intention, a traditional literature review is intended for the purpose of gaining a general understanding of a topic whereas a systematic review addresses a clearly defined research question in a very specific way towards a highly specific conclusion. A systematic review has enough rigor that the findings are more likely than not helpful, both when considering the implications for practice, and when developing policy and subsequent research.
A further disadvantage is that systematic reviews also require more time because they are developed by the search, screening and selection of studies. Though traditional reviews are often faster than systematic reviews, speed can come at the expense of the comprehensiveness and reproducibility of the latter.
When to Apply Which Type of Review
Whether to conduct a systematic vs. traditional literature review is determined by your research scope. Narrative reviews Narrative literature reviews are most appropriate when a new topic or theoretical perspective is being considered and one must include information from less controlled studies or research studies not designed for the expected synthesis.
Limitations of Traditional Literature Reviews
Although some flexibility is provided by traditional literature reviews they have [a number of] drawbacks. One type of problem is subjectivity, so that a researcher can sometimes bias himself by choosing studies favoring his own beliefs (if he had one) at the time of the search or missing results that do not comport with his predilections. This bias may lead to imbalance of evidence and lower certainty of the evidence. Furthermore, traditional reviews may not be transparent in their approach, with limited information on the methods used, thereby not aiding in replicating these results and questioning whether they reflect a thorough search and synthesis of evidence, rather than relying on a biased approach.
Advantages of Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews, however, have several advantages. The systematic way conducted would make a variety of studies being included and then decreases in reporting bias occurring. Since it outlines topics for inclusion and exclusion, it is possible to know that the review is an accurate reflection of the evidence. Furthermore, systematic reviews usually include quality assessment, which distinguishes between high- and low-quality evidence that can provide a more robust base for decision making in research, clinical work, and decision making in relation to policies.
Meta-Analysis and its Role in Systematic Reviews
One of the key factors that distinguishes many systematic reviews is the possibility of conducting a meta-analysis, which would allow statistical pooling of results of available studies. It enables researchers to understand patterns to measure the overall impact of interventions, and to detect trends that would not have been visible in single studies. The statistical power of a review is enhanced by meta-analysis, and its confidence improved, with the widespread preference for systematic reviews when more quantitative, precise evidence is needed.
Integrating Both Approaches
In some areas of study, it may be advantageous to combine aspects of both systematic literature reviews and traditional reviews. A narrative review, e.g., can furnish a general sense of the topic and identify areas where research is lacking, enabling a more narrowly-focused systematic review to be conducted on a specific research question. The juxtaposition of the two combines the more narrative and open approach of the traditional review with the systematic and trusted method of reviewing for reliability.
Future Directions in Literature Review Methodology
The trend of literature review methodology is still changing. With the development of digital databases, artificial intelligence and machine learning, researchers have new methods available to make systematic reviews more efficient and to minimize human error in the systematic review process. Hybrid approaches that integrate qualitative synthesis with systematic methods are also gaining popularity, which enable richer interpretation without the associated loss of rigor. It enables researchers to remain up to date with developments in evidence synthesis methodologies and techniques.
Conclusion
There is a place for both the systematic and traditional literature review. Narrative reviews are a flexible method of reviewing concepts and trends, while systematic reviews are a transparent, reliable approach with well-established procedures for synthesizing evidence. Differences between the two approaches are described so that authors can choose the most suitable method for their study and the review brings knowledge in the field forward in an effective manner.
For more updates and details visit our Facebook Page!
FAQs
1. Which sort of reporting is superior to the other for scholarly research?
This will vary depending on what you’re studying. The conventional literature review is suitable for addressing general topics and constructing theoretical models, while the systematic review is more appropriate for generating accurate evidence-based finding about special research issues.
2. Is it possible to do a classical literature review in medical science?
Yes, though it is not as thorough as a systematic review. For health research, systematic reviews are typically preferred given their transparent and replicable process for a valid and reliable evidence underpin clinical or policy decision making.
3. How much longer does it take to do a systematic review than not?
Systematic reviews generally require several months to more than a year because of tedious search, screening and analysis. Traditional literature reviews may be conducted more quickly, as they tend to be more flexible and narrative.
4. Is meta-analysis always present in systematic review?
Not necessarily. Although many systematic reviews have a meta-analysis for pooling studies results, there are also other side reviews that concentrate on qualitative synthesis, especially when the studies are to varied for the quantitative analysis.
5. Are both types of reviews acceptable for publication in peer-reviewed journals?
Yes, you can publish systematic and traditional literature reviews. Journals usually favor systematic reviews because of rigor and reproducibility, and traditional reviews, whose merit is the conceptual analysis, historical framework, the narrative integration.





